|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Internal links SEO is one of the most important strategies you can use to improve your website’s visibility.
Lucky you, that’s exactly what I am going to cover in this chapter.
Welcome back and let’s get started.
It’s not just about search engines, though.
Internal linking also helps users navigate your site better, keeping them engaged longer and boosting your page views.
Let’s dive into why this is important and how you can do it effectively.
Why are Internal Links Important for SEO and User Experience?
Before we jump into the strategies, let’s talk about why internal linking is essential. Internal links connect different pages on your site.
These links help search engines understand the structure of your website and discover new pages.
Search engines, like Google, use internal links to crawl your website.
When you have strong internal linking, it helps boost the SEO ranking of your pages. Think of it like building a roadmap for Google to follow.
If a page has more external links pointing to it, Google assumes it’s important and should rank higher.
It’s a simple yet effective way to spread the authority around your website.
But it’s not just about search engines.
Internal linking also enhances user experience.
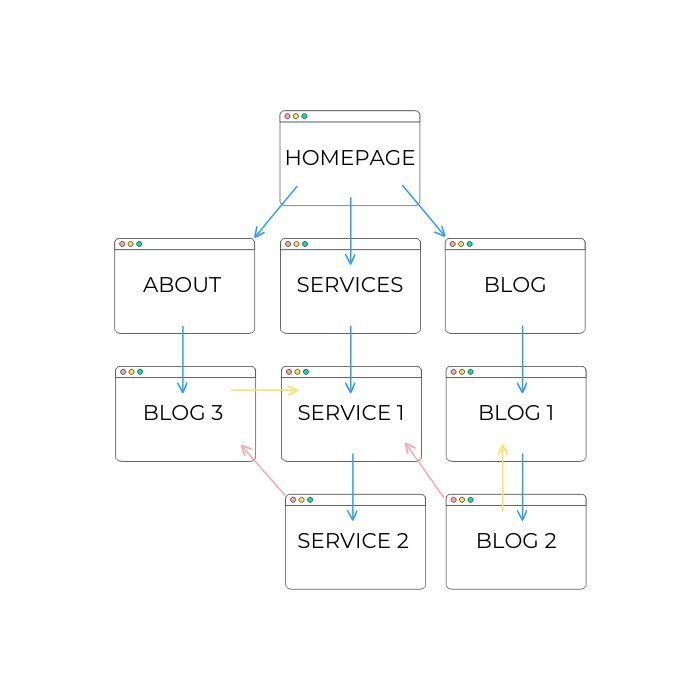
Think about it from a visitor’s perspective.
If they land on a blog post about a topic they’re interested in and you provide links to other useful content, they’re more likely to stay longer.
They’ll explore other related articles, products, or services you offer.
Longer visits = higher engagement.

Strategies for Creating an Effective Internal Linking Structure
Now that you understand the importance of internal linking for both SEO and user experience let’s talk about strategies to make it work.
Here are a few simple steps you can take to build an internal linking structure that helps your site grow.
1. Plan Your Internal Linking Structure
Before you start linking pages, it’s a good idea to map out your site’s structure.
A simple way to do this is by creating a hierarchy.
At the top, you have your homepage.
Below that, you’ll have your main categories, subcategories, and individual pages.
This is sometimes called a pyramid structure.
For example:
- Homepage: This is the main page that external links to your most important sections.
- Categories: These are broad topics that group related pages.
- Subcategories: These get more specific and target niche topics within your main categories.
- Individual Pages: Blog posts, product pages, and other specific content.
This structure helps users and search engines navigate your site in a logical way.
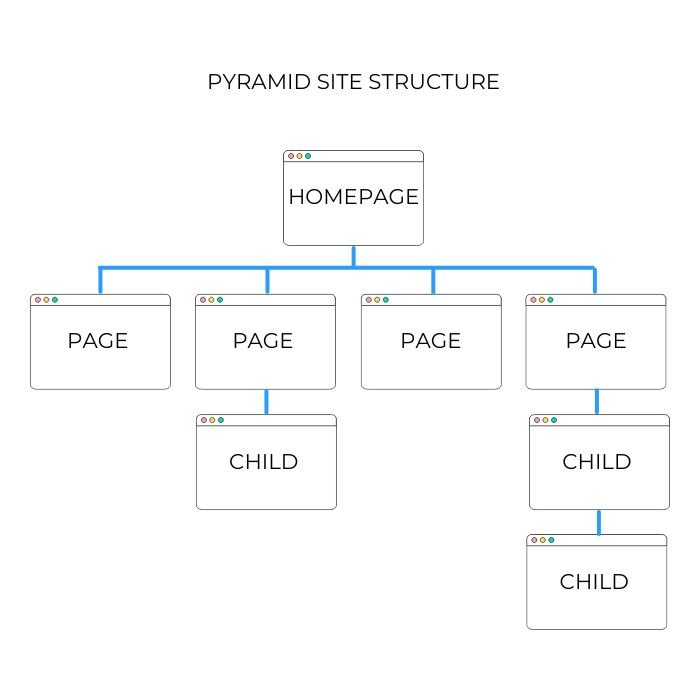
When we, at Antibe, work with clients, we always recommend starting with a clear map of your site.
It helps prevent confusion and ensures that the most important content gets the attention it deserves.
2. Link from Pillar Content to Supporting Pages
One effective internal linking strategy is to create pillar content, which is a long, comprehensive page covering a broad topic.
It serves as a foundation and external links to more specific, supporting pages.
Let’s say you run a WordPress site about healthy living. Your pillar page might be “The Ultimate Guide to Healthy Living.”
This page would then external link to smaller, more specific posts like “How to Start a Balanced Diet” or “Best Exercises for Busy People.”
This strategy helps build topic authority. Search engines recognize that you’re covering a topic in-depth, which can improve your overall rankings.
Some Stats to Back It Up:
- Sites using pillar-cluster models saw a 24% increase in organic traffic after implementing the strategy (HubSpot).
- Longer pages with lots of internal links are more likely to rank on the same page of Google (Ahrefs).
3. Use Descriptive Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink.
It’s important to use descriptive anchor text because it gives both users and search engines an idea of what the linked page is about.
For example, instead of saying “click here,” say “read our guide on healthy diets.” This makes it easier for Google to understand the relevance of the link.
Be careful not to over-optimize your anchor text. While it’s important to use keywords, don’t use the same exact text every time.
Google may see this as spammy, which can hurt your SEO.
4. Balance Links Between Popular and Less Popular Pages
Not all your content will be equally popular, and that’s okay.
Internal linking is a great way to balance out your traffic.
Link from high-traffic pages to lower-traffic ones to spread the link juice around. This helps your less popular pages get noticed by both search engines and users.
We often do this with clients at Antibe. For example, if we have a blog post that’s consistently bringing in traffic, we’ll use it to link to newer or less visited posts.
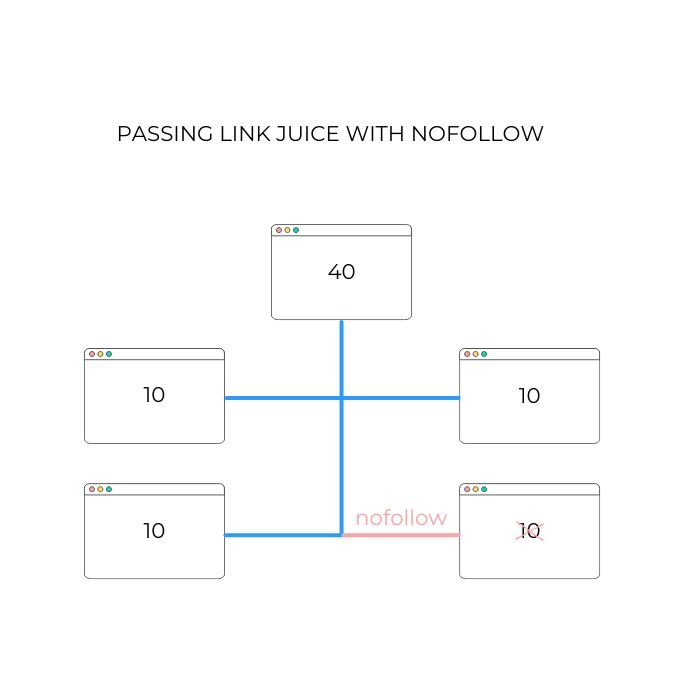
For example if you have a webpage that has 40 UR and you link to 4 pages, that will pass 10 UR to each of them.
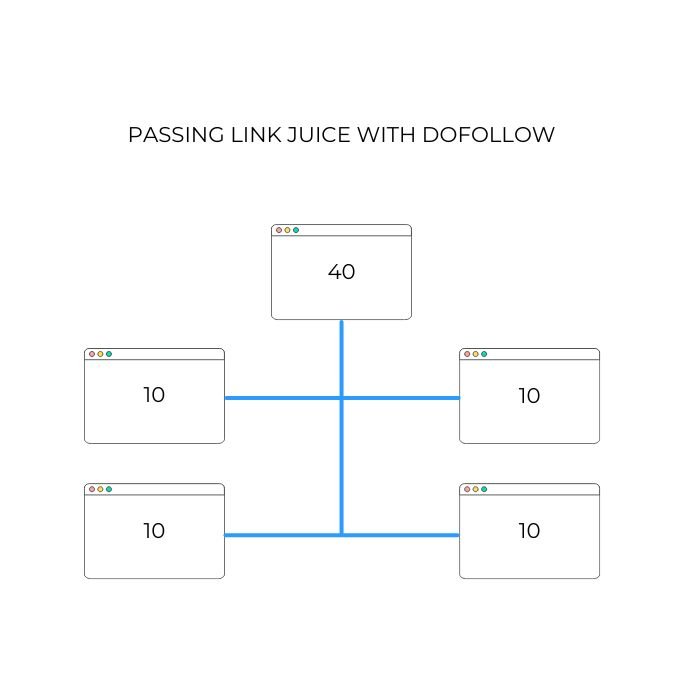
It’s an easy way to boost the visibility of those pages without creating brand-new content.
However, if you link to one of the page with a nofollow link, that will still pass on 10, but the crawler will not take it into consideration.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
While it’s important to have a strategy, there are also some best practices to keep in mind when building your internal linking structure.
These tips will help you stay on track and avoid common mistakes.
1. Keep Links Relevant
When you’re linking between pages, make sure the links are relevant.
If someone is reading about how to build internal links for SEO, don’t external link to a page about cooking recipes.
Keep it within the same topic or niche. This ensures that both users and search engines understand the connection.
2. Add Internal Links to Old Posts
Whenever you publish new content, it’s a good idea to go back and add internal links to your older posts.
This not only helps spread link juice but also breathes new life into old content.
For example, if you wrote a blog post about SEO strategies a year ago, link it to your new post about internal linking.
This keeps the older post relevant and shows search engines that it’s still valuable.
3. Use Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are a great way to enhance your site’s navigation.
They are small links at the top of a page that show users the path they took to get there.
For example, Home > Blog > SEO Tips > Internal Linking.
Breadcrumbs help users understand where they are on different pages on your site and provide easy links to go back to previous sections.
They also help search engines better understand your site’s structure.
Comparison of Popular Internal Linking Plugins for WordPress
When it comes to WordPress, plugins can make your life a lot easier.
Here’s a quick comparison of some of the most popular plugins to help with internal linking.
| Plugin | Features | Cost |
| Yoast SEO | Internal link suggestions, breadcrumb support | Free, Pro version ($89/year) |
| Rank Math | Internal link suggestions, link counter | Free, Pro version ($59/year) |
| Link Whisper | Automatic internal link suggestions, detailed reports | Paid ($77/year) |
| SEO Press | Internal linking recommendations, nofollow management | Free, Pro version ($39/year) |
We recommend Yoast SEO if you’re serious about building a solid internal linking structure. It’s easy to use and helps automate the process, making it ideal for larger sites.
How to Audit Your Internal Links Effectively
Auditing your internal links is one of the best ways to ensure that your website’s SEO strategy stays strong.
Over time, content changes, new pages are added, and some links may break or become less effective.
Regular internal link audits ensure that your website remains easy to navigate for users and highly accessible for search engine crawlers.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to audit your internal links thoroughly, along with useful tools, statistics, and expert tips.
Step 1: Use Crawling Tools to Identify Broken or Misplaced Links
The first step in an internal link audit is to crawl your site.
Crawling tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs Site Audit, or SEMrush can help you quickly find broken internal links, misplaced links, and other issues that could hurt your SEO.
These tools simulate how search engines crawl your website, giving you a detailed report of what’s working and what’s broken.
How Screaming Frog Can Help
Screaming Frog is one of the most popular SEO tools for site auditing. It crawls your website’s URLs and highlights issues like:
- 404 errors (broken links)
- 302 redirects (temporary redirects that could harm SEO if not managed)
- Missing H1 or meta descriptions, which can impact SEO rankings
Key Tip
Set Screaming Frog to scan your entire website, including deep pages. This way, you’ll get a comprehensive view of all internal links, even the ones buried within older blog posts.
You’ll be surprised how often broken links accumulate over time, especially on large sites.
Step 2: Find and Fix Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are other pages on your website that aren’t linked from any other pages.
Search engines struggle to find and index these pages because no internal links are targeting them.
If you’re not careful, orphan pages could fall through the cracks and never show up in search results, despite having valuable content.
How to Find Orphan Pages
To locate orphan pages, use tools like Google Search Console or Screaming Frog.
Google Search Console can show you other pages that are indexed but not receiving any traffic, which may indicate an orphaned page.
Screaming Frog can be used to compare crawled pages with your sitemap to identify pages that exist but have no types of internal links pointing to them.
Internal Links Important Stats
- Orphaned pages are 28% less likely to rank in search results compared to pages that are well-linked (Ahrefs).
- Websites with fewer orphan pages tend to have 10% better crawlability, leading to higher overall SEO performance (Semrush).
Key Tip
Once you’ve identified your orphan pages, integrate them into your internal linking strategy by linking to them from related content or important pillar pages.
This not only helps search engines discover the pages but also increases their visibility to users.
Step 3: Analyze Your Internal Link Distribution
Your internal links should be strategically distributed across your site.
The most important pages, such as pillar content or high-converting pages, should have more internal links pointing to them.
Use your audit to ensure that key pages are receiving enough attention and that your internal links are not overly concentrated in just a few places.
How to Analyze Link Distribution
In tools like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog, you can generate reports that show the types of internal links pointing to each page.
Make sure your most valuable pages (those that convert well or drive significant traffic) are getting plenty of internal links.
Likewise, avoid linking too heavily to less important or outdated content.
Stats to Keep in Mind
- Pages with at least 3-5 internal links perform better than pages with fewer links (LinkWhisper).
- Websites that strategically link their top-performing content can see a 10-15% increase in organic traffic within months (DataBox).
Key Tip
Use this audit to build out your pillar-cluster model, ensuring that your high-ranking pillar pages link to relevant subtopics.
For example, if you have a pillar page about “SEO Basics,” link out to related posts like “Keyword Research” and “On-Page Optimization.”
Step 4: Check for Link Depth and Crawl Depth Issues
Search engines prioritize pages that are easily accessible within a website.
If it takes too many clicks to reach a particular page, it may be less likely to get indexed or ranked highly.
Analyzing your crawl depth is essential to ensure that no page is too far removed from the homepage.
How to Check Crawl Depth
Use tools like Ahrefs Site Audit or SEMrush to analyze your website’s crawl depth.
These tools will show how many clicks it takes to reach each page from the homepage.
Ideally, important content should be no more than 3 clicks away from the homepage to ensure it gets indexed properly.
Key Tip
If you find important pages buried too deep within your site, consider updating your successful internal linking strategy to surface those pages more prominently.
Common Mistakes to Avoid for Internal Links SEO
Even though internal linking is straightforward, some common mistakes can actually hurt your SEO rather than help.
Mistake 1: Too Many Links on One Page
While few internal links are beneficial, too many links on one page can dilute their effectiveness.
Google may not be able to tell which links are important if there are hundreds on a single page.
Keep it simple; use an internal link to only the most relevant content.
Mistake 2: Broken Internal Links
Nothing hurts user experience like clicking on an internal link that leads to a 404 error page.
Use tools like Yoast SEO or Link Whisper to regularly check and fix broken internal links and fix them immediately.
Mistake 3: Using Generic Anchor Text
Avoid using phrases like “click here” or “read more” as anchor text.
These are missed internal linking opportunities to tell search engines and users what the linked page is about.
Always make your anchor text descriptive.
How We Can Help You?
At Antibe, we specialize in business transition marketing, which means we know the value of a well-structured website.
Whether you’re launching a new site or revamping an old one, we’ve got the tools and expertise to help you improve your internal linking structure.
We focus on boosting both your SEO and user experience, so your site performs better overall.
We’ve helped numerous businesses see measurable improvements in their SEO rankings simply by refining their internal linking strategy.
Our team works directly with you, ensuring that every internal link adds value to your site.
Conclusion
Internal links SEO is one of the easiest ways to improve both your SEO rankings and user experience.
By following best practices, you can make sure your internal linking structure is working for you.
We specialize in helping businesses improve their internal linking strategies to drive more organic traffic and keep users engaged.
Whether you’re just starting or looking to enhance your existing structure, we’ve got the tools and expertise to help you succeed.
Remember, it’s not just about the number of internal links; it’s about creating a logical, user-friendly structure that helps both search engines and visitors find the information they need.
If you’re currently working on something, I’d love to hear about it! Let’s connect!
Feel free to reach out ( hristijan@antibe.com )
Frequently Asked Questions
What are internal links in SEO?
Internal links SEO are hyperlinks that point from one page on your website to another page within the same website.
They help both search engines and users navigate your site.
For example, when you write a blog post and internal link to another post on a related topic, that’s an internal link.
For SEO, internal links are crucial because they show search engines how your content is connected and which pages are important.
These internal links distribute internal link equity (sometimes called “link juice”) across your pages, helping to improve the ranking potential of your content.
In simpler terms, think of them as a map that tells search engines and users how to move around your site.
You’ll love how easy it is to guide people through your best content just by adding a few well-placed external links!
How many internal links are good for SEO?
There’s no exact number of internal links that you need to follow, but a good rule of thumb is to aim for 3 to 5 internal links per blog post or page.
This ensures that your pages are well-connected without overwhelming your readers or search engines.
It’s important to focus on quality, not just quantity.
Make sure the internal links are relevant and lead the user to content that will add value to their experience.
For example, linking a page about “best SEO tools” to another page on “SEO basics” makes sense, while linking it to a page about “baking cakes” wouldn’t help.
We always ensure our internal links make sense for both readers and search engines.
So, don’t worry about hitting an exact number, but rather think about how the internal links make your content easier to explore.
Does internal linking boost SEO?
Absolutely! Internal linking is one of the easiest ways to improve your site’s SEO.
When you use internal links, you help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your site, making it easier for them to index your pages.
Pages with more contextual links pointing to them tend to be viewed as more valuable and can rank higher in search results.
Internal links also keep visitors and pages on your site longer, which improves user engagement and signals to Google that your site is worth exploring.
We’ve got the tools to help you build an internal linking structure that can really give your SEO a boost.
Can too many internal links hurt SEO?
Yes, too many internal links can hurt your SEO. If a page has too many contextual links, it can confuse search engines about which pages are important.
Google has said that while internal links are beneficial, overloading a page with hundreds of links can dilute their value.
You’ll want to balance the number of links.
Aim for quality over quantity. Make sure each internal link you add is useful and adds value to the user’s journey.
You don’t want visitors feeling lost in a sea of unnecessary links, right?
Focus on keeping things simple and relevant.
So, while internal links are great, moderation is key.
